01 Jun Dividends: Definition in Stocks and How Payments Work
However, it’s not a good look for a company to abruptly stop paying dividends or pay less in dividends than in the past. Dividends are often expected by shareholders as their share of the company’s profits. Dividend payments reflect positively on a company and help maintain investors’ trust. The dividend yield of a stock is the dividend amount paid per share and is expressed as a percentage of the company’s share price, such as 2.5%.
Dividend declared journal entry
A percentage of profits can be paid as dividends, and a percentage can be reinvested back into the business. Dividends are always considered taxable income by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) regardless of the form in which they’re paid. If Company X declares a 30% stock dividend instead of 10%, the value assigned to the dividend would be the par value of $1 per share, as it is considered a large stock dividend. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
Types of Dividends
In this case, the dividend payments come to your brokerage and are deposited in your brokerage account. The vast majority of dividend stocks pay dividends quarterly, although there are some companies that make dividend payments monthly and a very small number that make annual and semiannual dividend payments. A dividend payment is the distribution of a company’s profits to its shareholders. Dividends are usually paid in cash but sometimes in company stock, and companies often use them to return excess profits to investors.

Impacts to your financial statements
- For example, if a company issues a stock dividend of 5%, it will pay 0.05 shares for every share owned by a shareholder.
- A stock dividend may be paid out when a company wants to reward its investors but either doesn’t have the spare cash or prefers to save it for other uses.
- A stock dividend functions essentially like an automatic dividend reinvestment program (more on that below).
- Non-qualified dividends, on the other hand, are taxed at the individual’s ordinary income tax rate, which can be higher.
- Stock dividends dilute the ownership percentage but do not change the total value of equity held by each shareholder.
- A company with a long history of dividend payments that declares a reduction or elimination of its dividend signals trouble.
The dividend per share calculation shows the amount of dividends distributed by the company for each share of stock during a certain time period. Keeping tabs on a company’s DPS allows an investor to see which companies are able to grow their dividends over time. The most reliable American companies have a record of growing dividends — with no cuts — for decades. Examples of companies that pay dividends include Exxon, Target, IBM, Sherwin-Williams Co., and Johnson & Johnson. An elite list of S&P 500 stock companies called the dividend aristocrats have increased their dividend every year for at least 25 years. By comparison, high-growth companies, such as tech or biotech companies, rarely pay dividends because they need to reinvest profits into expanding that growth.
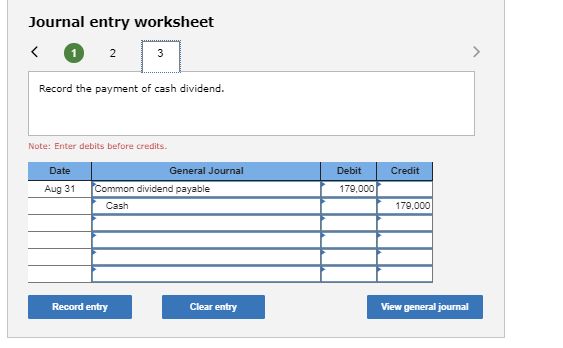
Simply put, a dividend payable is the dividend approved by the shareholders in the annual general meeting. The calculation methods are different for different shares and based on their preferences. Once the previously declared cash dividends are distributed, the following entries are made on the date of payment.
Azam: MACC probing FashionValet founders’ assets and use of Khazanah and PNB investment funds
11% preference share capital of $500,000, consisting of 5000 shares of $100 each. Suppose a corporation currently has 100,000 common shares outstanding with a par value of $10. First Majestic is a publicly traded mining company focused on silver and gold production in Mexico and the United States. Consolidated AISC in the third quarter was $21.03 per AgEq ounce, representing a 3% decrease from $21.64 per AgEq ounce in the previous quarter. This was primarily attributable to lower cash costs along with lower worker participation costs.
Retained earnings are the cumulative net income less any dividends paid to shareholders over the life of the company. The debit to retained earnings represents the reduction in the company’s earnings as a result of the dividend declaration. The corresponding credit to dividends payable signifies the company’s obligation to pay the declared dividends to its shareholders.
When the small stock dividend is declared, the market price of $5 per share is used to assign the value to the dividend as $250,000 — calculated by multiplying 500,000 x 10% x $5. When a stock dividend is issued, the total value of equity remains the same from the investor’s and the company’s perspectives. The dividend discount model or the Gordon subject to change growth model can help investors choose individual stocks. These techniques rely on anticipated future dividend streams to value shares. A shareholder may be indifferent to a company’s dividend policy, especially if the dividend is used to buy more shares. If a dividend payout is seen as inadequate, an investor can sell shares to generate cash.
Dividends payable are a manifestation of a company’s profitability and its board of directors’ decision to distribute a portion of earnings to shareholders. This distribution is a signal of confidence in the company’s financial stability and future prospects. ABC Limited has 12% cumulative preference shares of $5 million, consisting of 50,000 shares of $100 each.
A dividend is the distribution of some of a company’s earnings as cash to a class of its shareholders. Dividends are typically credited to a brokerage account or paid in the form of a dividend check. The dividend check is mailed to stockholders but can be directly deposited to a shareholder’s account of choice if preferred. Regular dividend payments should not be misread as a stellar performance by the fund. For shareholders, the tax treatment of dividends depends on the type of dividend received. Qualified dividends, which are typically paid by U.S. companies or qualifying foreign companies and held for a specific period, are taxed at the lower long-term capital gains tax rates.
Companies can either reinvest their earnings in themselves or share some or all of that revenue with their investors. Dividends represent income for investors and are the primary goal for many. Another potential benefit of DRIPs is that some companies offer stockholders the option to purchase additional shares in cash at a discount. Investors can acquire additional stock holdings at an advantageous cost compared to buying shares in cash through a brokerage firm and there’s the added benefit of not paying commission fees. Some companies with solid histories of paying dividends have established quarterly dividend payment dates. IBM usually pays its dividends on the 10th of March, June, September, and December.

