Introduction to Clinical Data Management: Managing Data from Clinical Trials
Clinical Data Management (CDM) is critically important in clinical research because it ensures the generation of high-quality, reliable, and statistically sound data from clinical trials.
This is the foundation upon which decisions about the safety and efficacy of new drugs or medical devices are made.
The primary goal is to produce trustworthy data for medical research by minimising errors and inconsistencies and by ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Key activities include study setup, data capture using electronic systems, quality control, and data lock for analysis.
What is Clinical Data Management?
Clinical Data Management (CDM) is the process of collecting, validating, cleaning, and managing data from clinical trials to ensure the results are high-quality, reliable, and statistically sound.
Why is Clinical Data Management Important?
- Clinical Data Management is essential for:
- Data Quality and Integrity
- Regulatory Compliance
- Patient Safety
- Efficient Drug Development
- Foundation for Analysis
Key Concepts in Clinical Data Management—
- Data Quality and Integrity: This is paramount. Data must adhere to the ALCOA principles: Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate. This ensures the trustworthiness of the trial results.
- Regulatory Compliance: All processes must comply with international and local regulations, most notably Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and the FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11 (for electronic records and signatures).
- Audit Trail: A secure, computer-generated, time-stamped electronic record that independently documents the history of actions, additions, deletions, or alterations to the electronic data. It ensures traceability of all data changes.
The CDM Career Path Progression
- Clinical Data Management roles are generally structured by increasing levels of responsibility, scope, and strategic oversight.
- A career in Clinical Data Management (CDM) offers diverse and growth-oriented opportunities within the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device, and Contract Research Organisation (CRO) sectors. The career path typically progresses from entry-level coordination to strategic, senior management roles.

Clinical Data Management Career Path
| Career Level | Common Job Titles | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level |
|
Data Entry and logging, initial quality control checks, CRF/eCRF tracking, and supporting data-related documentation. |
| Mid-Level |
|
Lead the CDM process for a study (Protocol to Database Lock), develop the Data Management Plan (DMP), design eCRFs, program and test Edit Checks, and manage query resolution. |
| Senior/Specialist |
|
Oversight of multiple studies, coordination of global teams, advanced database programming (building, validation, and reporting), complex data reconciliation, and applying advanced analytics/AI. |
| Management/Executive |
|
Strategic oversight of the entire CDM function, process improvement, resource management, vendor oversight, and ensuring departmental compliance with global regulations. |
Essential Skills for Success
To excel in Clinical Data Management, professionals need a mix of technical proficiency and strong soft skills:
- Technical Knowledge:
-
- CDM Process: Deep understanding of the entire clinical trial and data management lifecycle.
-
- EDC Systems: Proficiency in using Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems (e.g., Medidata Rave, Oracle Clinical).
-
- Regulatory Guidelines: Expertise in ICH-GCP and country-specific regulations like 21 CFR Part 11 (for electronic records).
-
- Data Standards: Familiarity with data standards like CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium).
-
- Programming/Analytics (for advanced roles): Skills in SQL, SAS, R, or Python for data extraction, manipulation, and analysis.
- Soft Skills:
-
- Attention to detail is critical for ensuring data accuracy and quality.
-
- Communication: Excellent verbal and written skills for managing queries with site staff and coordinating with cross-functional teams (Biostatistics, Clinical Operations).
-
- Problem-Solving: The ability to investigate and resolve complex data discrepancies.
Why Should You Opt for Clinical Data Management as Your Career?
💊 Key Reasons to Choose Clinical Data Management
The field of CDM is essential to drug and device development, which translates into several significant career advantages:
High Demand and Job Security
- Essential Function: CDM professionals are the guardians of data quality in clinical trials. Without their work, a clinical trial cannot be submitted to regulatory bodies like the FDA. This makes the role non-negotiable and recession-resistant within the healthcare sector.
- Industry Growth: The market for clinical trials and pharmaceutical R&D is continuously expanding globally, which drives a corresponding high demand for skilled data managers to handle the increasing volume and complexity of patient data.
- Diverse Employers: Opportunities are available across numerous sectors, including Pharmaceutical and Biotech companies, Contract Research Organisations (CROs), academic research institutions, and healthcare IT firms.
Excellent Career Growth and Compensation
- Defined Progression: The career path is well-defined, offering clear routes for advancement from entry-level roles (e.g., Clinical Data Coordinator) to senior and leadership positions (e.g., Lead Clinical Data Manager, Director of CDM, or CDM Project Manager).
- Competitive Salary: Due to the specialised nature of the work—combining life science knowledge with technical data skills—salaries in CDM are typically lucrative and highly competitive within the life sciences and IT fields.
- Specialisation: As you gain experience, you can specialise in areas like Clinical Database Programming (using SAS, SQL, etc.), Data Science/Analytics, or regulatory compliance, further increasing your market value.
Impactful and Purpose-Driven Work
- Contribution to Medicine: CDM is at the core of new treatment development. By ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and integrity of clinical trial data, you directly contribute to the safe and effective approval of new drugs and medical devices that improve patient lives.
- Hybrid Skills: The role provides an ideal intersection for those with a background in Life Sciences (Pharmacy, Biotechnology, Nursing, etc.) who also have strong technical and analytical skills. It allows you to apply scientific knowledge in a data-driven, technologically advanced environment.
Work-Life Balance and Flexibility
- Office/Remote-Based: Unlike roles such as Clinical Research Associates (CRAs), who must travel frequently to sites, most CDM positions are office-based or now offer remote/hybrid work options, which are often cited as a key benefit for work-life balance.
Accessibility for Life Science Graduates
Clinical Data Management (CDM) is highly accessible for Life Science Graduates and is considered one of the best career paths for those looking to transition from a theoretical science background into the data and technology side of the healthcare industry.
Eligible Life Science Degrees
The core requirement for a career in CDM is an undergraduate or postgraduate degree that provides a deep understanding of the human body, diseases, and the drug development process.
- Highly relevant degrees include:
- Pharmacy: B. Pharm, M. Pharm (offers a strong foundation in pharmacology, drug development, and regulatory affairs).
- Medicine & Allied Health: MBBS, BDS, BAMS, BHMS, Nursing, BPT.
- Life Sciences: B.Sc./M.Sc. in Biotechnology, Microbiology, Biochemistry, Biomedical Science, or other Life Science majors.
How Has the Industry Worked Out So Far?
The CDM industry, which is crucial for managing the data collected in clinical trials for new drugs and devices, has undergone a dramatic transformation, moving from slow, paper-based processes to highly efficient, digital, and intelligent systems.
The Initial Steps: Manual and Paper-Based (Pre-1990s)
- Process: Clinical data were collected on Paper Case Report Forms (CRFs).
- Challenges: The process was extremely labour-intensive, slow, and prone to error (e.g., transcription mistakes, lost documents, and manual query resolution).4 Data was not available for review until the paper forms were submitted, which caused significant delays.
The Digital Shift: Computerisation and EDC (1990s – Early 2000s)
Key Technology: Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems emerged.
Progress:
-
- Reduced Errors: Direct digital input into an electronic database eliminated manual transcription errors.
-
- Real-Time Access: Data became available to sponsors and monitors in real-time, allowing for quicker oversight and decision-making.
-
- Automation: Basic edit checks were introduced to automatically flag invalid or inconsistent data at the point of entry.
Centralized Management and Standardization (Early 2000s – 2010s)
Key Milestones:
-
- Clinical Data Management Systems (CDMS): These provided a more comprehensive platform that included EDC but expanded to manage the entire data lifecycle (collection, cleaning, validation, and analysis preparation).
-
- Standardisation: The adoption of standards from the Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) ensured that data structures were consistent across different systems and organisations, streamlining regulatory submissions.
-
- Regulatory Focus: Regulations like 21 CFR Part 11 reinforced the need for secure, traceable, and validated electronic records.
Integration and Modernisation (2010s – Present)
The industry has moved towards highly integrated and intelligent platforms:
| Feature | Progress and Impact |
|---|---|
| Integrated Platforms | Modern systems now combine EDC, CDMS, safety systems, and other tools into a unified platform (e.g., for managing labs, imaging, and patient-reported outcomes). |
| Data Sources | The industry now manages data from increasingly diverse sources, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs), wearable devices, and mobile apps (ePRO/eCOA). |
| Efficiency/Quality | Risk-Based Monitoring (RBM) was adopted, focusing monitoring efforts on the highest-risk data and processes, saving time and resources. |
| Technology Adoption | The rise of Decentralised Clinical Trials (DCTs), supported by flexible data collection methods, has made trials more patient-centric and global. |
| Future Drivers | Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are increasingly used to automate data cleaning, identify anomalies, and enhance predictive analytics, promising even faster and more accurate insights. |
This change has led to the creation of a huge number of job opportunities related to this sector. Clinical research, Pharmacovigilance, and Clinical Data Management courses make you a step ahead in standing and getting hired in this industry. The CDM market is moderately competitive and consists of several major players. Companies like IQVIA, ICON, Fortrea, Syneos, Parexel, and PPD hold substantial market share in the CDM market. The Asia Pacific market accounted for a significant industry share in 2024 and is poised to exceed USD 8.90 billion by 2034, according to a new report published by Global Market Insights, Inc.
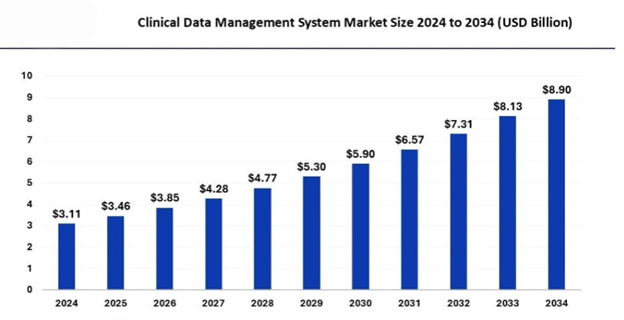
Job and career prospects
The growth in CDM is fast, which eventually leads to managerial and director roles with good pay packages.
The entry-level job for life science graduates/postgraduates is Clinical Data Coordinator/Associate (Entry-Level). CDCs are mainly involved in Data entry, query resolution, and tracking forms.
From there, career progression in CDM will typically grow with exposure, knowledge, and experience. Your role can vary from process expert, subject Matter expert, product quality lead, team leader, assistant manager, deputy manager, senior manager, general manager, director, vice president, Service Delivery Manager/lead, and many more. There is continuous growth in the field with an average 30% raise in salary every year. The yearly compensation for a career in CR is very go, od and the starting salary ranges.
Apart from these, your role can also involve a more in-depth technical part if you acquire the additional skills in CDM as below. Salary packages reach high with each role or designation up to 50-60 lakhs or more per annum based on experience, tenure, and knowledge and skills.
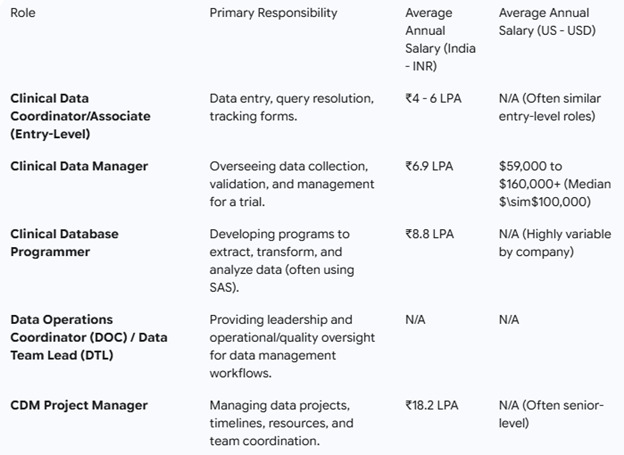
Growth Prospect:
The clinical data management field offers stable, high-demand, and rewarding career prospects for those with a background in life sciences, pharmacy, or medicine. The long-term growth prospects for the clinical research industry are exceptionally strong, driven by a convergence of scientific, demographic, and technological factors. This translates into a highly stable and expanding job market.
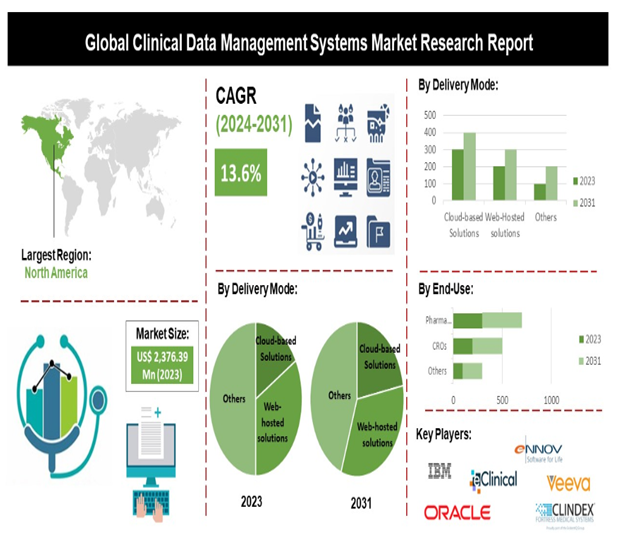

What Training programs/courses can be taken to become a Clinical Research Professional at Dysmech Clinical Services Pvt Ltd (DCS)
- Post Graduate Diploma in Advanced Clinical Research Management (CRM) (1 year) (9 months theory + practical & 3 months internship)
- Post Graduate Diploma in Clinical Research (CR) and Pharmacovigilance (PV) (1 year) (9 months theory + practical & 3 months internship)
- Post Graduate Diploma in Clinical Research (CR) and Clinical Data Management (CDM) (1 year) (9 months theory + practical & 3 months internship)
- Post Graduate Diploma in Clinical Research (CR) and Regulatory Affairs (RA) (1 year) (9 months theory + practical & 3 months internship)
- Advanced Diploma in Clinical Research Management (CRM) (6 months theory + practical & 1 month internship)
- Diploma in Health Technology Assessment (HTA) (6 months)
- Diploma in Good Clinical Practices (GCP) (6 months)
- Diploma in Advanced Clinical Research (CR) and Pharmacovigilance (PV) (6 months theory + practical & 1 month internship)
- Diploma in Clinical Research (CR) and Clinical Data Management (CDM) (6 months theory + practical & 1 month internship)
- Diploma in Clinical Research (CR) and Regulatory Affairs (RA) (6 months theory + practical & 1 month internship)
- Certificate course in Clinical Research (CR) (3 Months)
- Certificate course in Pharmacovigilance (PV) (3 Months)
- Certificate course in Clinical Data Management (CDM) (3 Months)
About Dysmech Clinical Services Pvt Ltd (DCS):
DCS is an educational research centre, a professional training and soft skill development organisation. Our company provides the best and state-of-the-art facilities and knowledge-sharing platforms, which are an exception in the CD.M
DCS offers specialised programs with industry exposure in international standards with the Drug Information Association (DIA)
Our faculty and guest lecturers are industry professionals, and they are adept at delivering their duties as needed by the students. Solving the queries of the students and taking them to the right path is what our faculty is masterful in.
The ambience and study environment at @DCS is one of the best compared to the other institutes providing Clinical Data Management courses in Pune.
The teaching staff @at DCS helps to learn the depth of this subject and course, and helps them get certified, which is internationally acclaimed in collaboration with some of the prestigious partne.rs
Drug Information Association, which adds volume to their profile and makes each of our students get a practical exposure to software tools along with theory classes whichich help them get trained and become proficient to enter the industry.
Students registered with us @DCS would have an excellent platform and knowledge to land in a good company or enterprise, and can boost their growth opportunities by availing the benefits of our wide network and contacts across companies and industries.
Looking at the growing demand for the courses, DCS has introduced the state-of-the-art curriculum,w hich will help our students cope with the requirements and pressures of the real job. For the benefit of working professionals and full-time students, the course is conducted every Saturday.
You can very well trust in our honest dealings.
So, when are you joining??
Check out the details and contact us today to be the leader of tomorrow.
